Learn About Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) The Modern Evolution in Vehicle Safety
What is ADAS?
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are cutting-edge technologies designed to enhance vehicle safety and driving convenience. These systems use sensors and cameras to detect potential hazards and assist drivers in avoiding accidents. By automating certain driving tasks and providing real-time alerts, ADAS can significantly reduce the risk of collisions and improve overall road safety.
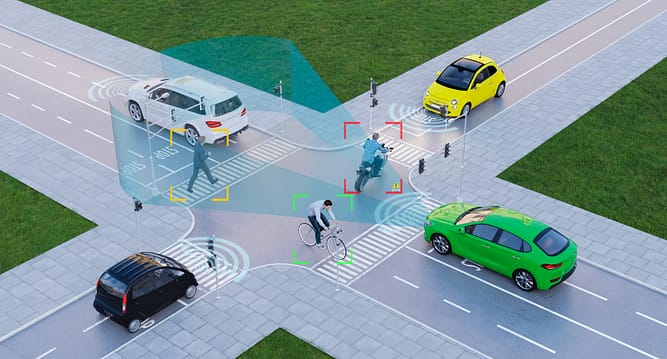
Firstly, the development of ADAS came about in response to the high rate of road crashes caused by human error. These systems aim to minimise human errors by automating and enhancing vehicle technology to assist and inform driver. ADAS features include adaptive cruise control, collision avoidance systems, lane departure warnings, and more. These features not only alert drivers to potential dangers but also take control of the vehicle if needed to prevent accidents.
More recent research indicates a both a growing adoption of ADAS in new vehicles by manufacturers, with approximately 33% of new vehicles in key markets already equipped with these features. It's Expected by 2030, that half of all new vehicles on the road will be equipped with some form of ADAS, highlighting the increasing importance of these technologies in improving road safety and driving efficiency.
ADAS Components
In modern vehicles, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) encompass a wide array of components designed to enhance safety and driving convenience. These systems utilise sensors, cameras, radars, and other technologies to monitor the vehicle's surroundings and assist the driver in various ways. Common ADAS components found in modern vehicles include:

History of ADAS
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) has evolved and is a fascinating journey that began over a century ago. While the concept of driver assistance has been around since the early 1900s, modern ADAS as we know them today started to take shape in the late 20th century.

Circa 2003, Honda made a significant advancement with the introduction of the first collision mitigation braking system. This technology used sensors to detect potential collisions and automatically applied the brakes to prevent or reduce the impact.
But, the debut of lane departure warning systems came in the mid-2000s, which alerted drivers when they unintentionally drifted out of their lane. This innovation aimed to reduce accidents caused by lane drifting.
And more recently in 2010, Tesla Motors made headlines with the introduction of the Tesla Model S, which featured advanced ADAS features like autopilot. This marked a major milestone in the development of semi-autonomous driving capabilities in consumer vehicles.
Today, ADAS technologies continue to evolve rapidly, with automakers and tech companies investing heavily in research and development. From automatic parking systems to traffic sign recognition, ADAS has become an integral part of modern vehicles, enhancing safety and driving comfort for millions of drivers worldwide.
ADAS - Levels of Assistance & Automation
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are revolutionising the driving experience, offering a range of features that enhance safety, convenience, and comfort. ADAS technologies are categorized into different levels based on the level of automation they provide, ranging from basic driver assistance to fully autonomous driving. Understanding these levels is essential for drivers to grasp the capabilities and limitations of their vehicles' ADAS systems.
ADAS Level 0 - No Automation
ADAS at this level provides warnings and information to the driver but does not control the vehicle. Examples include parking sensors and blind spot detection systems.
Understanding the different levels of ADAS is crucial for drivers to use these systems safely and effectively. While higher levels of automation offer more convenience, they also require a clear understanding of their capabilities and limitations to ensure safe operation.
FAQ
Below are some frequently asked questions to find answers to commonly asked questions about Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), including how they work, their benefits, common features, and more.
ADAS stands for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems. It refers to a set of safety features and technologies integrated into vehicles to assist drivers in various driving scenarios. These systems use sensors, cameras, radar, and other technologies to detect potential hazards and provide warnings or take autonomous actions to prevent accidents.
ADAS works by continuously monitoring the vehicle's surroundings and detecting potential dangers such as other vehicles, pedestrians, or obstacles. The system analyses this information and provides warnings to the driver or takes autonomous actions to avoid collisions. For example, if ADAS detects a vehicle in the driver's blind spot, it may provide a visual or audible alert to warn the driver.
ADAS offers several benefits, including improved safety, enhanced driver convenience, and reduced risk of accidents. By providing early warnings and assisting drivers in critical situations, ADAS can help prevent collisions, reduce the severity of accidents, and improve overall road safety.
Common features of ADAS include adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, automatic emergency braking, blind spot monitoring, rear cross-traffic alert, parking assistance, and traffic sign recognition. These features are designed to assist drivers in various driving scenarios and enhance vehicle safety.
ADAS features are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles, but they are not yet standard in all vehicles. Many new vehicles come equipped with some level of ADAS as either standard or optional equipment, but the availability of specific features may vary depending on the vehicle make, model, and trim level.
In some cases, ADAS features can be retrofitted to older vehicles using aftermarket kits or systems. However, retrofitting ADAS to older vehicles may require professional installation and calibration to ensure proper functionality and compatibility with the vehicle's existing systems.
ADAS systems are designed to be highly accurate and reliable, but their effectiveness may vary depending on various factors such as environmental conditions, sensor calibration, and system limitations. It's essential for drivers to understand the capabilities and limitations of their vehicle's ADAS features and to use them as intended.
Like other vehicle systems, ADAS systems may require periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. This may include sensor calibration, software updates, and regular inspections by qualified technicians. Proper maintenance is essential to ensure that ADAS systems function correctly and provide reliable assistance to drivers.
ADAS systems can potentially lower insurance premiums by reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall vehicle safety. Many insurance companies offer discounts or incentives for vehicles equipped with ADAS features due to their proven effectiveness in preventing collisions and reducing claims costs.
While ADAS systems offer significant benefits, they also have some limitations and potential drawbacks. These may include false alarms, reduced effectiveness in certain weather conditions, reliance on driver attention and intervention, and the need for regular maintenance and calibration. It's essential for drivers to be aware of these limitations and to use ADAS features responsibly.
Ready to ensure your ADAS is performing at its best?
Check out our ADAS calibration services to keep your vehicle's safety features in top condition.


